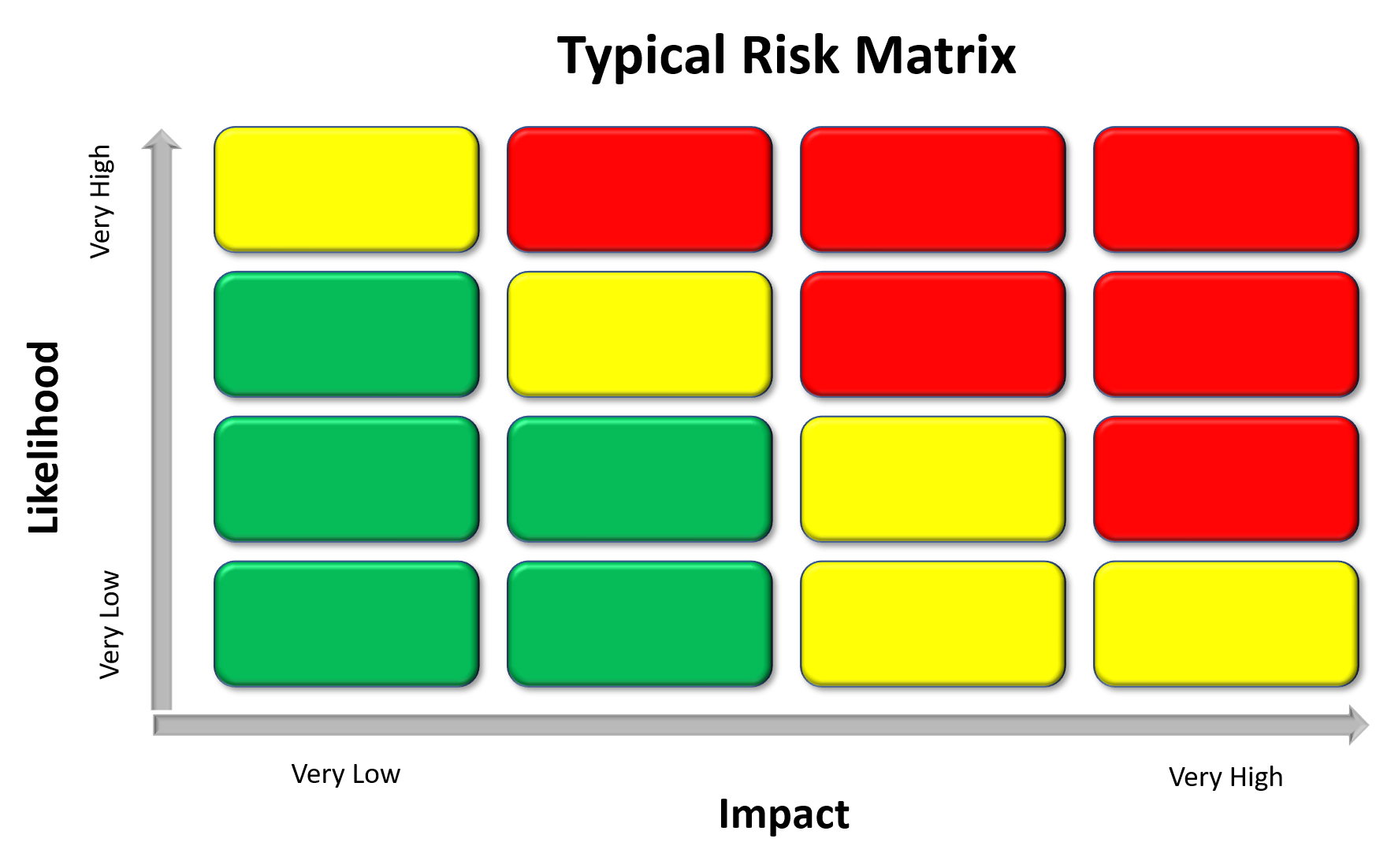
Reputation, Reputation, Reputation
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.” – Warren Buffett It is fascinating how many accident videos get posted to social media. Guess we all go to NASCAR races to see car wrecks. In some cases, videos are personal